singly linked list
A linked list is a data structure it stores every data you want either string or number. it is a list of order data just like an array but there is a big distinction in an array.
In an array, each item is --- it is indexed with a number. a linked list on the other hand just consists of elements with no indexes that are just pointing to the next element just like a train connection with a wagon where one is connected to the next wagon and that one connects to the next one but there are no indexes that we used to access things.

Therefore a linked post consists of a node. The node stores a piece of data like a string or number but it is also referencing the next node if there is no next node referencing then there are three properties we keep track of
The head is the beginning of the linked list
The tail is the end we don't keep track of any item in the middle we just keep track of the head and from the head, we can figure out the next one and then the next to the end
The length is the total number of the linked list to make things easier
Linked list | Array |
Do not have indexes | it is indexed and order |
connected via node with the next pointer | insertion and deletion can be expensive |
Random access is not allowed | can be quickly accessed at a specific index |
class Node {
constructor(val) {
this.val = val;
this.next = null;
}
}
class SinglyLinkedList {
constructor() {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
this.length = 0;
}
push(val) {
var newNode = new Node(val);
//if there is no Node create first node
if (!this.head) {
this.head = new Node(val);
// head and tail are the same
this.tail = this.head;
} else {
// take the current tail and take the 'next' propety and set it to new Node
this.tail.next = newNode;
// let the tail point to the new node
this.tail = newNode;
}
this.length++;
return this;
}
pop() {
if (!this.head) return undefined;
let current = this.head;
let newTail = this.head;
// traverse through the list
while (current.next) {
newTail = current;
current = current.next;
}
this.tail = newTail;
this.tail.next = null
this.length--
if(this.length === 0) {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
}
return current
}
shift() {
if(!this.head) return undefined
var currentHead = this.head
this.head = currentHead.next
this.length--
if(this.length === 0) this.tail = null;
return currentHead
}
unshift(val) {
var newHhead = new Node(val)
if(!this.head) {
this.head = newHhead
this.tail = this.head
} else {
newHhead.next = this.head
this.head = newHhead
}
this.length++
return this
}
}
Sometimes when we care about insertion and deletion especially if you are working with a long piece of data set with lots of information and you don't need a random access you just need to store it in a linked list
Doubly linked list
Basically, all that we do in a doubly linked list is to add a pointer to the previous node and the next node therefore each node points to two direction
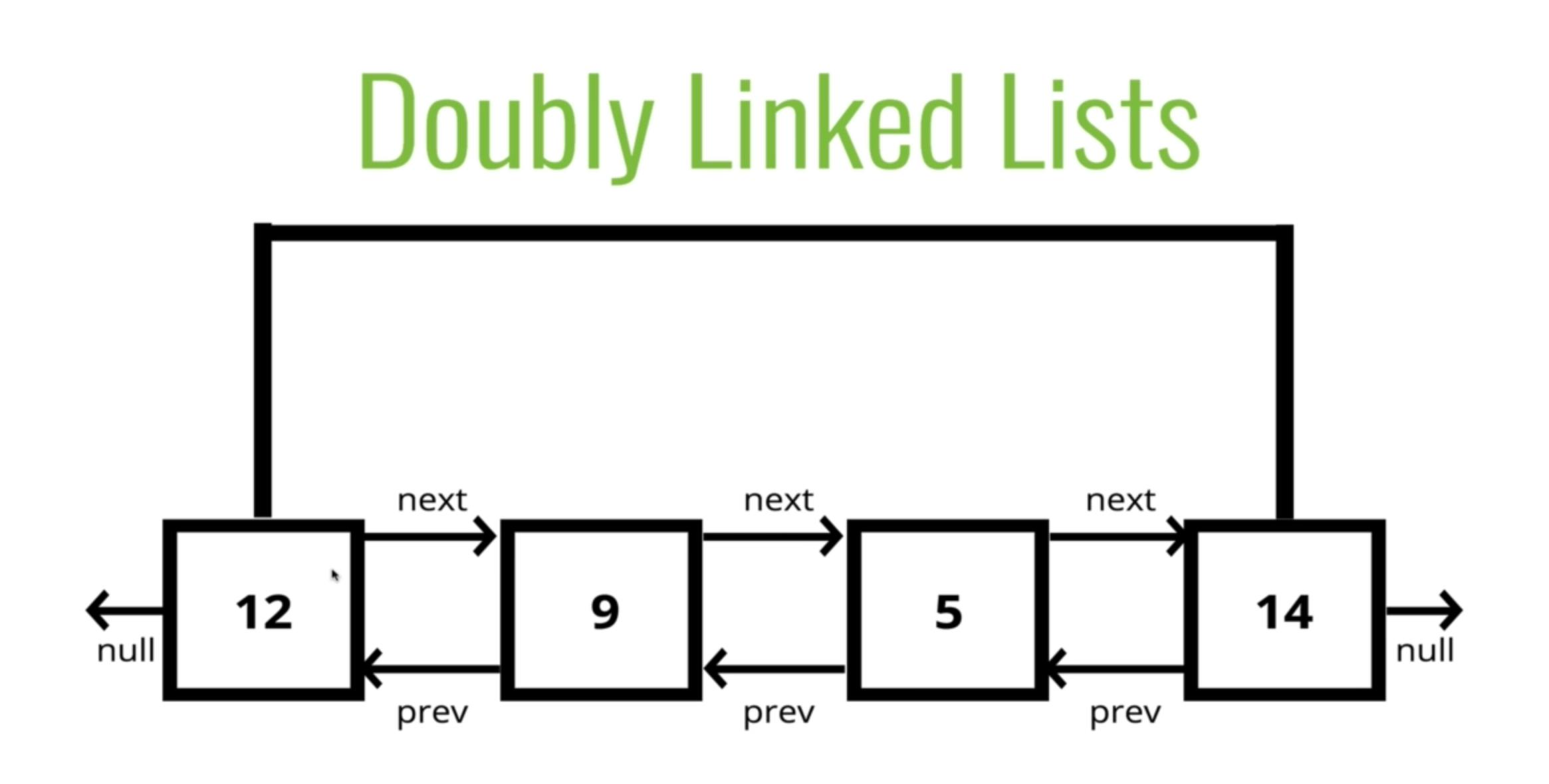
A Doubly linked list is almost Identical to s Singly liked list except every node has another pointer to the previous node and have two connection which makes a certain thing easier
class Node {
constructor(val) {
this.val = val
this.next = null;
this.prev = null;
}
}
class DoublyLinkedList {
constructor() {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
this.length = 0;
}
push(val) {
const NewNode = new Node(val)
if (!this.head) {
this.head = NewNode
this.prev = null
this.tail = this.head
} else {
this.tail.next = NewNode
NewNode.prev = this.tail
this.tail = NewNode
}
this.length++
return this
}
pop() {
if (!this.head) return undefined
const poppedNode = this.tail
if (this.length === 1) {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null
} else {
this.tail = poppedNode.prev
this.tail.next = null
}
this.length--
poppedNode.prev = null
return poppedNode
}
shift() {
if (this.length === 0) return undefined
const oldHead = this.head
shiftNode.next = null
if (this.length === 1) {
this.head = null
this.tail = null
} else {
const newHhead = oldHead.next
newHhead.prev = null
this.head = newHhead
oldHead.next = null
}
this.length--
return oldHead
}
unshift(val) {
const newNode = new Node(val)
if (!this.head) {
this.head = newNode;
this.tail = this.head
} else {
this.head.prev = newNode
newNode.next = this.head
this.head = newNode
}
this.length++
return this
}
}
It is better than a Singly linked list for finding a node and can be done half the time however it takes much memory considering the extra pointers
Big O and time complexity of linked list
| Singly Linked List | Doubly Linked List |
| Insertion O(1) | Insertion O(1) |
| Removal O(1) or O(N) it depends | Removal O(1) |
| Searching O(N) | Searching O(N) |
| Accessing O(N) | Accessing O(N) |
| less memory and less flexibility | more memory and more flexibility |
technically searching in a Doubly linked list O(N/2) but better still it is O(N)